CARTOGRAPHY IN HUNGARY
1999-2003

Hungarian National Committee (HNC) of ICA
edited
by Béla Pokoly, secretary
Department
of Lands and Mapping, Ministry of Agriculture and Regional Development
Institute
of geodesy, Cartography and Remote Sensing
Mapping Service of the Hungarian Defence Forces
Ministry
of Defence Mapping Company
prepared for the
12th General Assembly of the International Cartographic
Association
21st International Cartographic Conference:
Cartographic Renaissance
Durban, South
Africa, 10-16 August, 2003
CARTOGRAPHY IN HUNGARY 1999-2003
Contents
1. Tasks and organisation of Hungarian national
mapping
1.1. Act 76 of 1996 on Surveying and Mapping
Activities
1.2. Organisation of civilian mapping
1.3 Organisation
of military mapping
1.4. Topographic Mapping
1.4.1.1. Civil
Topographic Analogue Maps
1.4.1.2. Digital
Topographic Map Products of the Civil Lands and Mapping Administration
1.4.2. 1:25,000 to 1:250,000 scale military
topographic maps
1.5.
Mapping databases, elevation models
1.5.1. Digital
Topographic Database at 1:200,000 (DTA-200)
1.5.2. Digital
Elevation Models (DDM-10
and DDM-50)
1.5.3. Digital
Mapping Database (DTA-50)
1.5.4.
GIS
1.5.5. Gazetteer of Hungary
1.6. Remote Sensing for the National Economy
1.6.1. Scope of
activities at FÖMI Remote Sensing Centre :
1.6.2. National Crop Monitoring
and Production Forecast Programme (CROPMON 1997)
1.6.3. Area-based Subsidy
Control by Remote Sensing (1999-)
1.6.4. Development
of the Physical Block based Hungarian Land
Parcel Identification System (LPIS) for IACS on Pilot Areas (ProMePAR)
1.6.5. Additional
applications implemented on the CROPMON basis
1.6.6. CORINE Land Cover 1:50 000
1.6.7. Aerial
photography in civilian mapping: Aerial Photography of Hungary 2000
1.6.8. Aerial
photography in military mapping
2. Map publishing enterprises
3. Map collections, events on map history
3.1. The Map Collection
of the National Széchényi Library
3.2. The
Cartographic Collection of the Maproom of the Hungarian Institute and Museum of War
History
3.3. Report on the Events
Related to Map History in Hungary between 1999 and 2003
4. Institutes of Higher Education in Cartography
4.1. Report of
the Activities of the Department of Cartography, Roland Eötvös University of Budapest
(ELTE), between 1999-2003
4.1.1.
Introduction
4.1.2.
Training
4.1.3.
Sub-program for Cartography of the Doctoral School of ELTE
4.1.4.
Research
4.1.4.1. Aspects of representation in
thematic cartography (digital maps - electronic atlases)
4.1.4.2. Education in Cartography
4.1.4.3. Theoretical Cartography
4.1.5. The
Department’s other activities in ICA
4.2. Further institutions
of higher learning in Hungary related to cartography:
4.2.1. The Department of
Geoinformatics, College of Surveying and Land Management at the University of
West Hungary
4.2.2. Budapest University of Technology and Economics
5. Major Cartographic Events and News
in Hungary 1999-2003
6. The Hungarian National Committee of ICA
1. Tasks and organisation of Hungarian national mapping
1.1.
Act 76 of 1996 on Surveying and Mapping Activities
The scope of
state mapping, charting and geodesy (MC&G) tasks and issues on the implementation
of them are provided in Act 76 of 1996 on Surveying and Mapping Activities.
According to this act, the following tasks are to be considered as state base
ones:
– supplying the country with state maps;
– supplying the defence forces with maps;
– handling, storing, maintaining and providing
state base data;
– fulfilling the tasks arising from international
commitments;
– determining and filing geographical names as
well as providing data from them;
– MC&G related technical R+D activities.
In the interest
of mapping provision it is the state's responsibility to provide for state base
works. State base works are as follows:
– creating and continuous updating of state
surveying base maps and their index maps;
– creating and continuous updating of state
topographic maps;
– creating and maintaining of control point
networks;
– surveying of national borders;
– determining and filing geographical names
according to special acts and in co-operation with the Hungarian Committee on
Geographical Names.
According to Joint decree No. 21/1997 (12 March) between
the Ministry of Agriculture and the Ministry of Defence on the
implementation of the act the task of supplying the country with state maps has been allocated to the Institute
for Geodesy, Cartography and Remote Sensing (FÖMI), the Mapping Service of the
Hungarian Defence Forces (MS HDF) and the Ministry of Defence Mapping Company
(MoD Mapping Company) as central MC&G organisations.
The way and
scheduling of the implementation of the creation of state topographic maps, the
establishment of the surveying base of the country as well as standardisation
and regulation–taking into account the recommendations of the Coordination
Committee on Map Supply–is stated in a joint directive of the two ministers.
The way of
handling and providing surveying and mapping state base data as well as fees of
data provision, examination and backing of surveying tasks with special aim and
other public proceedings are provided in the Joint decree No. 63/1999 (21
July) between the Ministry of Agriculture and Regional Development, the
Ministry of Defence and the Ministry of Finance on handling and providing
MC&G state base data and on fees on certain administrative services.
1.2.
Organisation of civilian mapping
The
civil surveying and mapping activities and the land affairs are administered by
a governmental institutional network (consisting of one institute with
nationwide competence and 136 land offices with territorial competence) and a
public non-profit company, all being supervised by the Department of Lands and
Mapping at the Ministry of Agriculture and Regional Development (DLM/MARD).
This administration is responsible for establishing, maintenance and supplying
of the geodetic control networks, the large scale base maps including the
cadastral ones, the land registry, land protection and valuation, the
topographic maps of selected scales and the remote sensing. Special emphasis is
given to the tasks related to the implementation of the National Programme of
the Adoption of the Acquis Communautaire (NPAA).
The
Department of Lands and Mapping as supervising body is organised into four
divisions with the following main responsibilities:
§
Division
of Surveying: tasks relating to control point networks, national cadastral and
topographic maps as well as regulations and rules on national mapping and surveying.
§
Division
of Land Registration: real property registration, land area data supply, legal
measures pertaining the dept, and revises the appeals against land office
decisions.
§
Division
of Land Protection and Land Valuation: tasks relating to licensing of
non-agricultural use of croplands, control of utilisation obligation of
croplands, support of land restoration and land use as well as supervision of
measures on land consolidation.
§
Division
of Land Control and Development: control of land administration activities,
technical upgrade of the land offices IT development, co-ordination of the NPAA
framework, developments in GIS, spatial data infrastructure (SDI), remote
sensing.
The
above mentioned works are carried out by the following organisations:
§
Institute of Geodesy, Cartography and Remote Sensing (FÖMI)
as governmental organisation with nation-wide competence,
§
19 County
Land Offices (CLO) and the Budapest Land Office as governmental organisations
with territorial competence,
§
116
District Land Offices (DLO) and the Capital Districts Land Office as governmental
organisations with territorial competence,
§
Office for
National Cadastral Programme, as non-profit organisation.
1.3 Organisation of military mapping
The independent
Hungarian military mapping dates back to 4 February, 1919.
As of January
2001, the military MC&G tasks are implemented by two independent military
organisations.
The basic task
of the Mapping Service of the Hungarian Defence Forces is to plan state
base tasks and works in the responsibility of the minister of defence and
having them implemented as well as carrying out official tasks in its sphere of
authority. The Mapping Service of the Hungarian Defence Forces provides for the
execution of the tasks necessary for defence map supply and professionally
co-ordinates other sectors' defence related surveying and mapping activities
including standardisation and regulation issues.
– plans and organises mapping and military
geographic support of the armed forces;
– elaborates professional standards and
regulations;
– on special rule, provides for the authorisation
of survey camera aerial photography as well as the technical supervision of the
use of survey camera aerial photographs;
– operates military geographic and digital
topographic database, provides for the continuity of both map updating and the
filing of the changes on the maps;
– represents defence interests within the
Co-ordination Committee on Map Supply established for determining medium and long
term MC&G tasks of the country's map supply as well as scheduling and
co-ordinating these tasks;
– fulfils the tasks arising from international
commitments;
–
directs and supervises the professional
activities of MoD Mapping Company.
The basic task
of MoD Mapping Company is to implement state base tasks and works in the
responsibility of the minister of defence and having them implemented as well
as safeguard, handle and provide state base data and maps.
The tasks of MoD
Mapping Company are as follows:
– doing and having done surveying and mapping
works in the scope of state surveying and mapping tasks–first of all for the
interest of map supply of the defence forces–with national competency;
– safeguarding and handling state base data, base
maps and state topographic maps arising from the activities detailed in the
previous paragraph;
– map supply of the Border Guards, the Civil
Protection and the defence administrative and law enforcement bodies against
payment;
– producing military thematic maps (among others,
by modifying state topographic maps according to NATO prescriptions), military
geodetic control point catalogues and other special MC&G products in
analogue and digital form and in compliance with the demands of MS HDF;
– storing and providing state topographic maps,
mapping products and state base data in analogue and digital form for
utilisation by national economy;
– implementing aerial photography and other remote
sensing tasks or having them implemented;
– implementing tasks in connection with geodetic
support of military equipment and other weapon systems;
– field examining and maintaining state control
points for areas in MoD administration, preserving control points in control
point catalogue as well as replacing destroyed control points;
– operating an aerial film archive and providing
remote sensing materials;
– activities in connection with the technical
servicing the 'Open Skies Programme'.
1.4. Topographic Mapping
1.4.1.1. Civil
Topographic Analogue Maps
The
EOTR system of topographic map has been introduced in the 1970's by the civil
Lands and Mapping Administration to meet the demands, which could not be
satisfied earlier by military classified maps.
The
recent status of the analogue topographic map sheets of the civil Lands and
Mapping Administration is as follows:
§
at scale 1: 10 000: 4092 EOTR sheets
(100%)
§
at scale 1: 25 000: 267 EOTR sheets (25%)
(Terminated production),
§
at scale
1:100 000: 84 EOTR sheets (100%),
§
at scale
1:200 000: 23 EOTR sheets (100%).
The
production of EOTR topographic maps at scale 1:25 000 earlier was terminated. At
scale 1:10 000, the production and
updating has been finished and restarted in 2000. Updating the scales
1:100 000 and 1:200 000 is continuous from 1995 – in digital form.
The products at scales 1:10 000 and 1:100 000
have been supplied for the users continuously.
1.4.1.2. Digital
Topographic Map Products of the Civil Lands and Mapping Administration
In
the frame of the governmental base tasks and the EU-Harmonisation Programme the
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development supported the scanning and
georeferencing of 1:10 000 scaled topographic
sheets. This task was carried out in 2000 for the whole area of Hungary.
In
frame of the EU-Harmonisation Programme of the MARD the raster datasets of
relief of 1400 sheets in scale 1:10 000 have been
vectorized. The vector data is used for the production of a high resolution
(5m x 5m regular grid interval) Digital Elevation Model. As a first
step a "preliminary" DEM is produced (in same resolution), derived
only from the contour lines. The high resolution DEM will serve as a base for
the digital orthorectification of the aerial photographs, created the frame of
"National Aerial Photographic Programme 2000", and of the high
information for the National Topographic Programme.
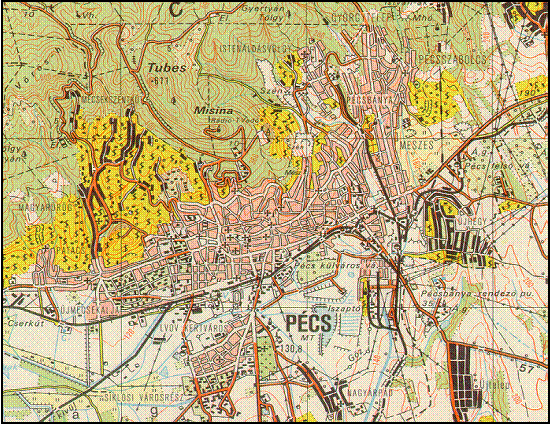
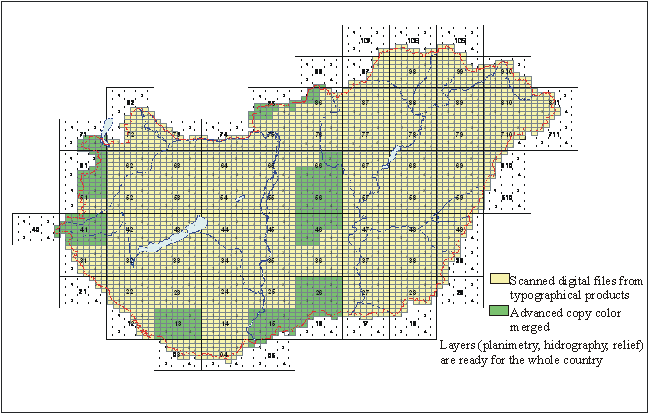 1:10 000
Analogue and Digital Topographical Map Status Description
1:10 000
Analogue and Digital Topographical Map Status Description
The
1:100 000 scaled topographic sheets of Hungary are available in digital (raster and vector)
format, too.
Recently,
the following products of the 1:10 000, 1:100 000 and
1:200 000 Digital Topographic Map series of EOTR are available:
DTA-10: Digital Topographic Map in scale 1:10 000
§
raster
data of contour
lines 4092 sheets (100%),
planimetry
4092 sheets (100%),
hydrography
4092 sheets (100%),
colour
prints 4092 sheets (100%),
§
vector
data of contour
lines 2940 sheets (72%)
§
§
preliminary
high-resolution digital elevation model 1056 sheets
(26%)
(DEM with 5m grid interval)
Fragment of the 1:10 000 Digital Topographic
Map
DTA-100: Digital Topographic Map in scale 1:100 000
§
raster
data of contour
lines 84 sheets (100%),
planimetry
84 sheets (100%),
hydrography
84 sheets (100%),
colour
prints 84 sheets (100%),
§
vector
data of contour
lines 84 sheets (100%),
planimetry 84 sheets
(100%),
hydrography 84 sheets
(100%),
§
digital
elevation model of Hungary
(DEM
with 100m x 100m regular grid interval) 100%
DTA-200: Digital Topographic Map in scale 1:200 000
raster
data of colour
prints 23 sheets (100%),
Fragment from the
1:100 000 Digital Topographic Map (© FÖMI)
1.4.2. 1:25,000
to 1:250,000 scale military topographic maps
Topographic maps belong to the most
important products of military MC&G. Classification of these maps were
'secret' until 1992, having made the civilian utilisation of them difficult to
a great extent. This restriction has been fully lifted by now, thus anyone can
have free access to military topographic maps.
The latest updating process of the
1:25,000; 1:50,000; 1:100,000 and 1:200,000 scale topographic maps began in
1983 and finished in 1997. The completed map sheets have full country coverage
at all scales. Updating of the content has been carried out on the basis of
aerial photographs and field verification. Smaller scale maps have been created
by derivation and generalisation.
Extract from a 1:25,000 scale topographic map sheet
A revision of content and conversion into digital form of
the 1:50,000 scale maps as well as re-editing of them onto WGS-84 datum and in
UTM projection is under way.
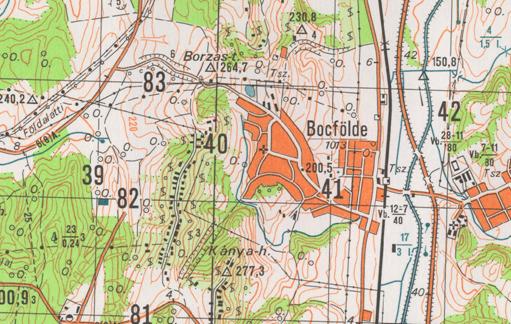
Extract from a 1:50,000 scale
updated topographic map sheet
The state acceptance process of the digitally transformed maps
accomplished at the Mapping Company of the Ministry of Defence is performed by
the Mapping Service of the Hungarian Defence Forces. As a first step, a
detailed map quality control and content revision is carried out; based on an
approved specification laid down to set the technological process of the production.
Following the result of the analysis the acceptance committee will make its
decision on the possible inauguration of the maps.
1.5.
Mapping databases, elevation models
Military mapping has been dealing with digital elaboration of maps since
the early 1980's. GAB, Geodetic Data Base and DTA-200, Digital Topographic
Database at 1:200,000 scale was completed in the second half of the 1980's,
followed by the 10 × 10 and a 50 × 50 m grid density Digital Elevation Models
(DDM-10 and DDM-50, respectively) and the DTA-50 Digital Mapping Database at
scale 1:50,000.
1.5.1. Digital
Topographic Database at 1:200,000 (DTA-200)
Creation of the DTA-200 database commenced in 1988. Since that time
this database has been used by several institutions as the basis for their
autonomous thematic database.
Extract from DTA200 data
base
The updating of
the database was carried out in 2000 and, as from 2002, the DTA200 database
under the name HUNET200 is accessible on the Internet, too (www.topomap.hu).
1.5.2. Digital
Elevation Models (DDM-10 and
DDM-50)
The Digital Elevation Model holds
height data above sea level for grid points of a 10 × 10 m and a 50 × 50 m grid
for the territory of Hungary. The
total extent of the data file with 10 × 10 m grid density is 2.5 GByte, with 50
× 50 m density is 100 MByte. The database is available in DTED Level1 and
Level2 formats as well.
1.5.3. Digital
Mapping Database (DTA-50)

The most significant work is the DTA-50 database founded on the
1:50,000 scale topographic map series. As a
general skeleton map, on the one hand, it renders possible the automatic
processing of topographic maps, and, on the other hand, it can be used as basis
of a future GIS application. Of course, as a result of conversion of
cartographic nature usual line representation as well as legend representation
are also feasible as a basic requirement for topographic maps.
The Digital Mapping Database contains some 900
features in the following categories:
Ä marginalia;
Ä control
points;
Ä settlements;
Ä facilities
(industrial, mining, telecommunication, etc.);
Ä bridges and
crossings;
Ä hydrography;
Ä hydrographic
and shipping facilities;
Ä relief;
Ä vegetation
and soils;
Ä
boundaries.
Extract from
DTA-50 database
Extract from a
1:50,000 topographic map sheet produced using the DTA-50 database
DTA-50 forms the mapping base
of several significant databases accessible on the Internet. A new version,
revised in content, will be available by the end of 2003.
1.5.4.
GIS
A
significant task will be the creation of Hungary's vector format GIS database at a scale answering to 1:500,000 and,
based on this database, the production of a Global Map data file for the
territory of the country.
MS HDF
makes every effort to contribute to modernisation of the Hungarian Defence
Forces by planning and evolving GIS systems as well. These systems combine GIS
achievements and products of the Mapping Agency of the Hungarian Defence Forces
as our legal ancestor. The main purpose of creation of GIS systems is to
promote implementation of complex military geographic examinations as well as
execution of various planning tasks. In addition to military information and
maps the systems also involve other thematic data, maps and multimedia
materials as characteristics of relevant areas.
1.5.5.
Gazetteer of Hungary
The
gazetteer-database under the responsibility of FÖMI contains 39 types of
geographical names, including the names of settlements, parts of the
settlement, the landscape, large units of the land woods, nature conservation
areas, relief and hydrography, names of remarked points (ruin, look out tower
etc.) as well as the names of the most important objects of traffic. It is the
Database of Geographical Names (FNT – Földrajzinév-tár).
The
database has two versions. The first one (FNT1) corresponds in quantity of
names approximately to the scale 1:40,000. This database was produced by the
use of 300 sources (maps, geographical literature, economical, statistical
sources), and each municipality had the chance to complete, modify the database
reflecting the local use of name. FNT1 covers the whole territory of Hungary, and changes are continuously updated.
The
second version (FNT2) corresponds in quantity and in the types of names used
roughly to the topographic map scale 1:10,000, with a readiness of 35%. It
covers the names of the database FNT1 with additions taken from large scale
topographical maps, cadastral maps, and other sources. The two parts of the
database comprise 105,000 records.
1.6. Remote
Sensing for the National Economy
1.6.1. Scope of activities at FÖMI
Remote Sensing Centre :
§
research
and development of technologies for the applications of remote sensing
primarily in the areas of agriculture and environmental protection/nature
conservation;
§
to provide
an efficient service as National Distributor in the distribution, processing, archiving
and utilisation of satellite and aerial remote sensing data, plus consulting
for the entire Hungarian users community in their RS projects.
FÖMI
RSC distributes all European, American, Indian and Russian satellite images and
has contracts with EURIMAGE, SPOTIMAGE, EUROMAP and the Russian Space Agency.
The national archive of satellite images is maintained by FÖMI RSC. Hungary is totally and repeatedly
covered by both SPOT and Landsat TM images. All digital satellite images of the
national archives are on CD. FÖMI RSC serves also as basic institution of the
Hungarian Space Office in Earth Observation.
Under
the direction of FÖMI RSC, a complete aerial photography of Hungary was carried out in 2000 (see
1.6.7.).
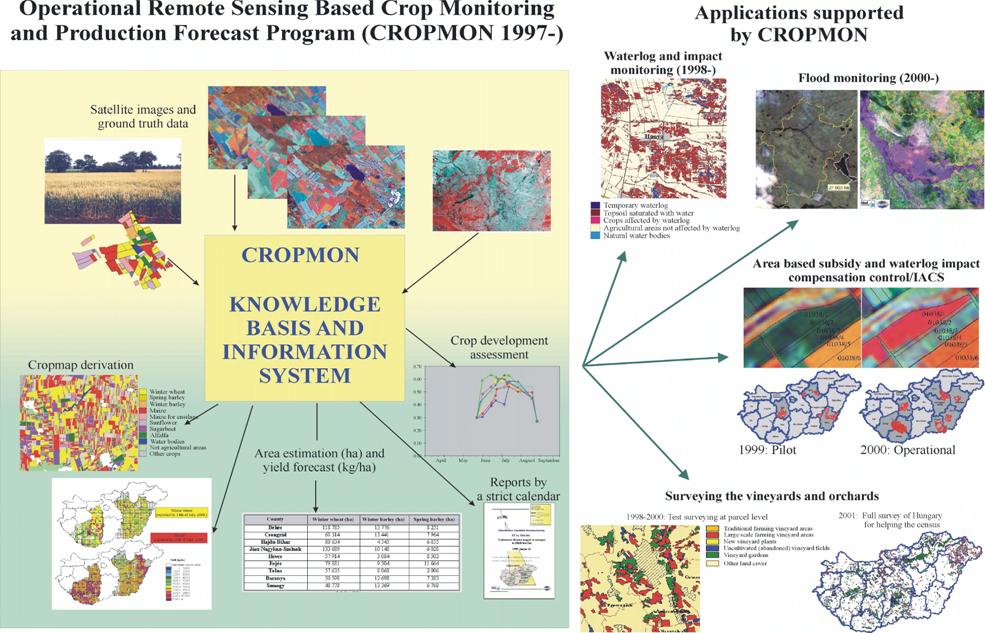
1.6.2. National Crop Monitoring
and Production Forecast Programme (CROPMON 1997)
In
the CROPMON Programme FÖMI RSC provides county and country level crop
production forecast based on remote sensing, measuring the areas and expected
yields of the 8 main crops. These crops together represent the 78-82 % of the
entire Hungarian cropland. The area and forecasted yield data are reported by a
strict calendar to the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development, 4-5 times
in a season, synchronised to the existing traditional production forecast
system of MARD.
CROP
AREA ASSESSMENT in CROPMON is based on the quantitative analysis of
multitemporal high-resolution images (Landsat TM and IRS-1C/1D LISS-III.)
providing precise crop area estimation at different levels: locally, in the
counties and for the entire country. The actual standard crop maps were also
provided to MARD.
CROP
YIELD FORECAST is accomplished by the application of FÖMI RSC developed model
which combines high-resolution satellite (Landsat TM and IRS-1C/1D LISS-III. or
SPOT) data and NOAA AVHRR time series. An HRPT receiving station had been installed
and operated in FÖMI RSC from May, 1998 to provide secure and real time NOAA
AVHRR data access for the models. FÖMI RSC provided yield estimates for the
counties and expanded them to Hungary using a regional-historical
correlation scheme. Because of the method applied, yield spatial distribution
maps could also be reported for the major crops. The basic elements of CROPMON
and the applications supported by CROPMON are shown on the next page.
1.6.3. Area-based Subsidy
Control by Remote Sensing (1999-)
The
principal national crop area based subsidy programme has been operative in Hungary, for many years now. Both the
crop subsidy and the ad-hoc partial loss compensation programmes that are
responses to extreme natural disasters (as e.g. for waterlog/flood damages),
work in sound legal framework. In 1997 FÖMI Remote Sensing Centre (FÖMI RSC)
initiated to MARD the introduction of remote sensing into the control of the
subsidy and partial compensation programmes. The subsidy controls were
performed on the CROPMON basis. Using FÖMI RSC’s operational remote sensing
based technology, a 3 counties sample was controlled by in a pilot project in
1999. The target area for RS based subsidy control was extended to a 7%, 4% and
5% ample of all the dossiers in 2000, 2001 and 2002 respectively (see next
page). On the basis of CROPMON the automatic control can be an important part
of the control of area based subsidies in Hungary.
1.6.4. Development of the
Physical Block based Hungarian Land Parcel Identification System
(LPIS) for IACS on Pilot Areas (ProMePAR)
The aim of the
project was to develop the country-wide Land Parcel Identification System
(LPIS=MePAR in Hungarian) on pilot sites with orthophoto based physical blocks
in harmony with the requirements of the Integrated Administration and Control
System (IACS) of the European Union.
ProMePAR is an
experimental system working on 6 settlements (3 counties) with voluntary
participation of the farmers. It builds on the existing facilities and
institutions and fulfils the EU requirements of the IACS area-based subsidy
handling through the work-flow of applications: farmer à office à
control à payment à farmer, with special emphasis on land parcel identification and
remote sensing control.
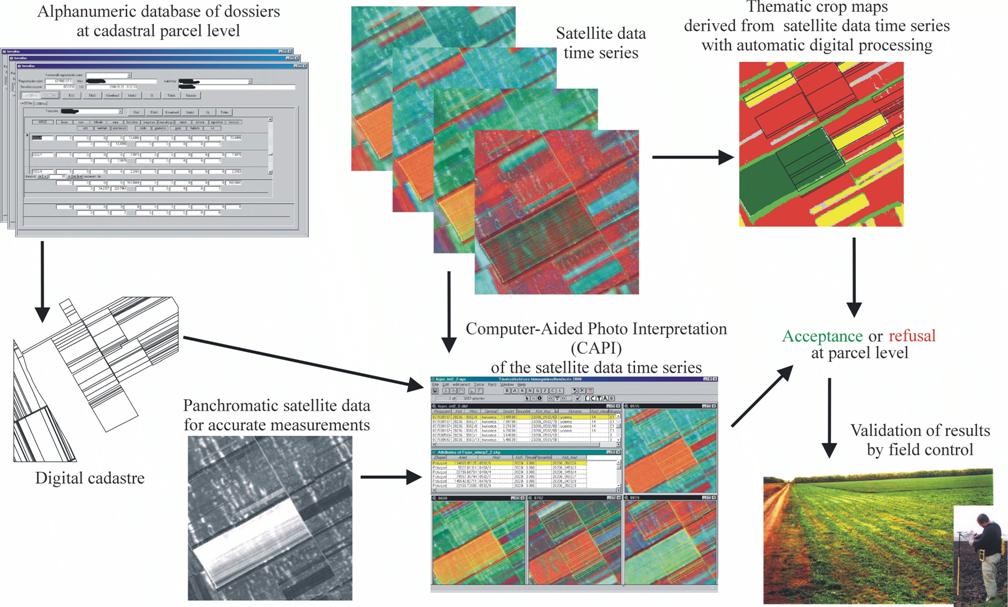
Major
results from ProMePAR as the basis for developing MePAR (the Hungarian LPIS):
§
EU
harmonic timeframe followed in the simulated EU harmonic area-based subsidy
payment process
§
orthophoto
generation and development of the physical block system (on 83 000 hectares)
with unique block identification, with delineation of non-cultivated areas
within the blocks, using satellite data time series and digital topographic
maps as supplementary information, giving the exact areas of the blocks in a
GIS system .
§
training
for the farmers and participating institutions
§
development
of the EU harmonic application forms, maps and guidelines together with the
other participants (county offices of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural
Development, Agricultural Intervention Centre)
§
preparation
and dissemination of orthophoto based physical block maps to the local agricultural
officials participating in the project
§
preparation
of orthophoto based block maps focused on the farmers’ agricultural parcels, and
sending of these through mail
§
reception
of the filled EU area-based subsidy forms, building up the databases and GIS
system
§
formal and
administrative control of over-declarations
§
remotely
sensed and field control of declarations
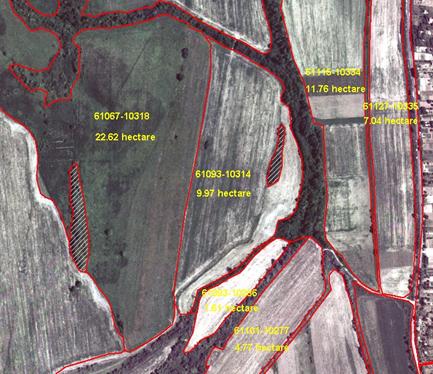
A part of
the orthophoto based physical block maps generated in the framework of the Hungarian Land Parcel Identification System
pilot project (ProMePAR)
1.6.5. Additional
applications implemented on the CROPMON basis
The
CROPMON makes the implementation of other monitoring programmes possible and
very cost effective on the same data, infrastructure and know-how basis at the
FÖMI RSC. WATERLOG AND IMPACT MONITORING Programme was launched for MARD that
covered the most affected 4 (1998) and 8 (1999) counties of about 4 million hectares.
Reliable waterlog maps and area measures were derived. Beyond the static status
assessment of the areas under water or having saturated soil, impact analysis
on the crops and the dynamism of changes could also be monitored
quantitatively. This assessment made use of high and medium resolution optical data,
that is Landsat TM, IRS-1C/1D LISS-III and WiFS as well. The resulted GIS data
base and printed maps were utilised by MARD intensively and proved to provide
fast, operational information for decision makers. Moreover remote sensing can
successfully be used at the parcel specific disaster compensation Programme for
the control of claims.
On
April 9, 2000 the Hungarian government
declared parts of eastern Hungary a disaster area due to the
serious flood event occurred on Hungary's
second largest river, the Tisza, and several tributaries.
FÖMI Remote Sensing Centre (FÖMI RSC) immediately began to start REMOTE SENSING
BASED FLOOD MONITORING operations with its available resources to help the
combat providing real time satellite data for the disaster area. As soon as the
NOAA data are recorded by the FÖMI RSC receiving station they got processed and
analysed in each day and transmitted directly to the Ministry of Transport,
Communications and Water Management, to the Regional Water Management network
headquarters in the most threatened areas plus the MARD. Even the slower and
less frequent high resolution data were acquired and processed relatively very
quickly to monitor and document the flood. According to the serious flood situation
along the upper part of Tisza river, FÖMI RSC could
mobilise its operational capabilities in spring 2001. At the first time after
53 years, the dike along river Tisza was breached by the water and
the water flooded the neighbouring areas through a 120-m wide gap threatening
tens of villages and thousands of people. The extent of flooded areas was
evaluated both on the Ukrainian and the Hungarian side and the high-, low- and
medium resolution flood maps were forwarded to the central and local management
authorities through electronic transmission.
In
addition to waterlog and flood, large area draught also hit Hungary in 2000 and
SATELLITE BASED DRAUGHT MONITORING were carried out for the detection of
extension and intensity of the draught at regional level based on NOAA AVHRR
data received at FÖMI satellite station. FÖMI provided a rapid draught report
to MARD including county level draught maps and temporal profiles of the most
affected crop (wheat) comparing actual data of 2000 to the data of previous
years having normal (1991) or draught conditions (1992, 1993).
FÖMI
RSC started to develop methods for SATELLITE BASED VINEYARD AREA ASSESSMENT to
monitor the real extent of production vineyard areas in Hungary. In 1997-98 this was carried
out in marked area of Mór, Etyek, Szekszárd wine-districts using high- resolution
satellite data (Landsat TM, SPOT, IRS-1C/1D LISS-III.).
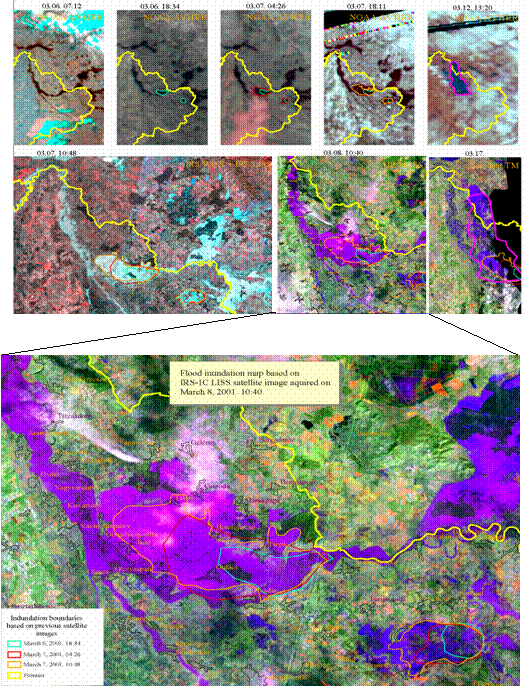
The elements of real-time flood monitoring carried out by
FÖMI RSC in 2001: low, medium and high resolution satellite images (a.).
Flood inundation map based on IRS-1C LISS satellite image
acquired
on March 8, 2001. 10:40,
with the previous inundation boundaries delineated on NOAA
AVHRR and WiFS data (b.).
In
December 2000, according to the EU regulations, the Hungarian Government
enforced by law, that the Central Statistical Office (CSO) has to conduct a
census in 2001. The census’s objective is to have up-to-date information about
the vineyard and orchard areas in Hungary. As a preparation for the census FÖMI RSC carried out the assessment
of the potential vineyard and orchard areas covering the whole country (19
counties) using high resolution satellite data in a very short, two months
surveying period in 2001. This high-tech RS-GIS technology gave a really good
basis for the census.
1.6.6. CORINE Land Cover 1:50 000
As
part of fulfilment of the government resolution on the “Development of
environmental information systems”, the implementation of the CORINE Land Cover
database at scale 1:50 000 (CLC50) has started
within the frames of the Acquis National Programme in 1999. The database
supports Hungary’s accession to the EU in
various programmes, such as the planning of sustainable agriculture, rural
development, agri-environmental planning and nature conservation.
The
CLC50 project has direct links to the standard European CORINE Land Cover
project, however most elements of the methodology were upgraded according to
the present level of technology in geo-data processing. The CLC50 nomenclature
used has been developed from the standard (level-3) nomenclature and includes
nearly 80 level-4 and level-5 classes, which have been adapted for Hungarian
conditions. Orthorectified SPOT-4 satellite images taken in 1998-99 and computer-assisted
photointerpretation allow for high positional accuracy of delineation. The 0.04
km2 size minimum mapping unit (0.01 km2 for lakes) provides enhanced geometric
detail. A rigorous internal supervision and an external quality control (performed
by the National Park Directorates and the counties' Plant Health and Soil
Protection Service) are other key elements of producing a high quality
database.
In
the table below, main parameters of the standard European CORINE project
(CLC100) and that of the CLC50 project are compared.
|
Parameter
|
CLC100, Hungary
|
CLC50
|
|
Nomenclature
|
standard EU
level-3
|
standard EU,
extended to level-4/5 according to natural conditions in Hungary
|
|
Methodology
|
hardcopy
photointerpretation
|
softcopy
(computer assisted) photointerpretation
|
|
Area
resolution
|
0.25 km2
for all categories
|
0.04 km2;
0.01 km2 for lakes
|
|
Linear
resolution
|
100 m
|
50 m
|
|
No. of classes
|
27 (out of 44)
|
80
|
|
No. of
polygons
|
24 000
|
>150 000
(estimation)
|
|
Positional accuracy
|
<100 m
(RMS)
|
<20 m (RMS)
|
|
Thematic reliability
|
>80%
|
>90%
|
|
Supervision
|
not
documented: direct corrections on plastic overlays
|
documented: remarks
on polygon level (instructions for corrections)
|
|
External
quality control
|
no
|
yes
|
|
Final product
|
topologically
structured database
|
Up
to now there were seven phases of the project resulting in about 86% of the
total area of the country mapped by December 2002:
|
Phase
|
funding
|
percent of
country mapped
|
|
1
|
ANP -1999 / Ministry of Agriculture
|
20
|
|
2
|
KAC / Ministry of Environment
|
10
|
|
3
|
Phare / Ministry of Environment
|
27
|
|
4
|
Econet / Ministry of Environment
|
9
|
|
5
|
ANP-2001 / Ministry of Agriculture
|
4
|
|
6
|
Econet / Ministry of Environment
|
3
|
|
7
|
ANP-2002 / Ministry of Agriculture
|
13
|
|
Total:
|
|
86
|
1.6.7. Aerial photography in civilian mapping: Aerial Photography of
Hungary 2000
Within
the frame of the European Harmonisation Programme of the Ministry of
Agriculture and Regional Development in the year 2000 - for the first time of
its history - aerial photography was completed for the whole territory of
Hungary during a short period of time at scale of 1:30 000 (see. Fig.11.).
As a result of this project more, than 7000 pieces of colour diapositive aerial
photos were taken, all of them were scanned and archived. This enormous amount
of data will serve as a “back-bone” of the nation-wide digital orthophoto
programme at scale of 1:10 000.
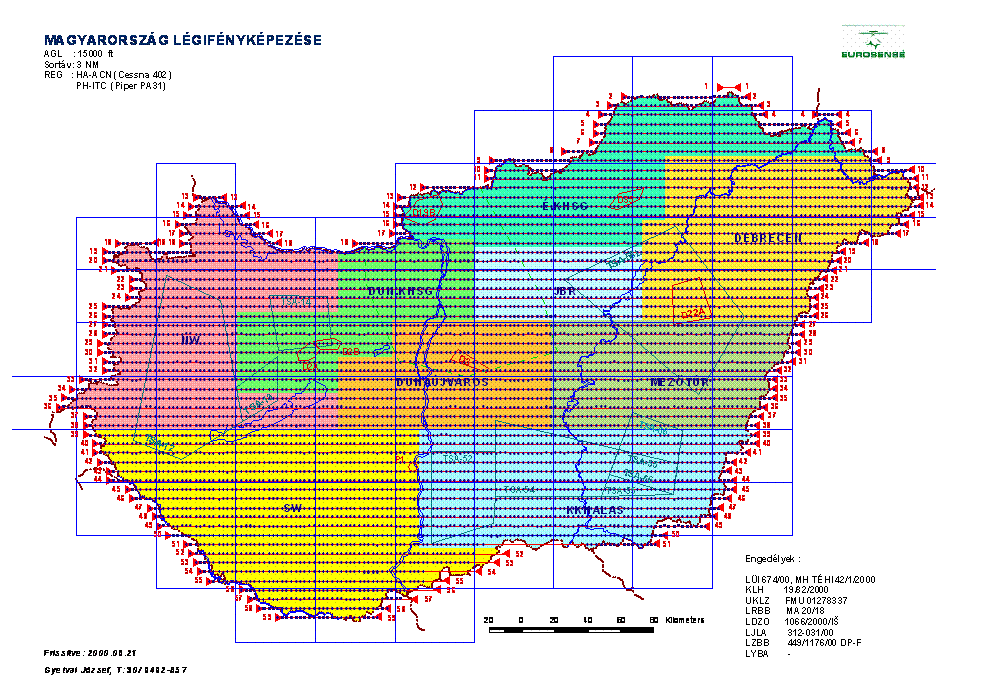
Aerial photography of Hungary
The
photography has to be suitable for several applications, as
§
Topographic
mapping,
§
Recording
of statement of several agricultural plants,
§
Establishing
of land use categories,
§
Delineation
of waste lands,
§
Surveying
of soil map contents,
§
Delineation
of soil erosion areas,
§
Mapping of
inland waters,
§
Regional
planning,
§
Forest inventory, management etc.
Based on the high-resolution digital
elevation model (5m-grid interval), FÖMI has started the orthorectification of
aerial photographs (ground pixel size 63 cm). The full technology is under
construction (see below)
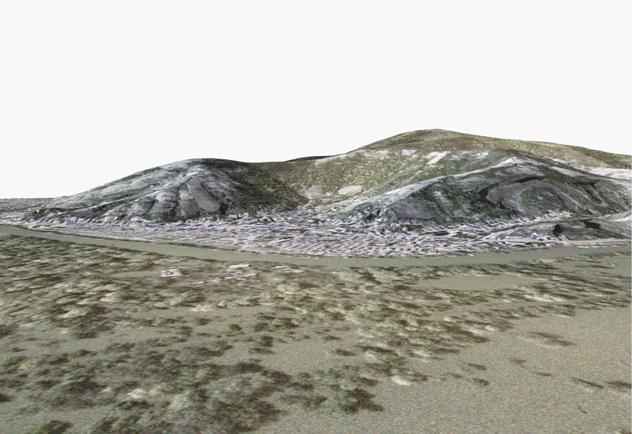

Digital orthophoto of Tokaj, draped to the high resolution DEM
1.6.8. Aerial
photography in military mapping
MoD Mapping NPC
produces survey camera aerial photographs in a significant number. According to
the last years' practice, 30% of the county is photographed every year at
1:30,000 scale that, besides mapping tasks, can be utilised in many other
fields of national economy. Information pertaining to aerial photographs can be
seen on the website of the Mapping Company of the Hungarian Defence Forces. An
Internet catalogue of survey camera made aerial photographs will make possible
–
the viewing and
storing technical data of survey camera made aerial
photographs,
–
the viewing of quick looks
of aerial photographs.
Quick
look images are published by means of the MrSid Image server. 800 × 800 pixel
quick look images of the aerial photographs are published with a 20× MrSid
compression.
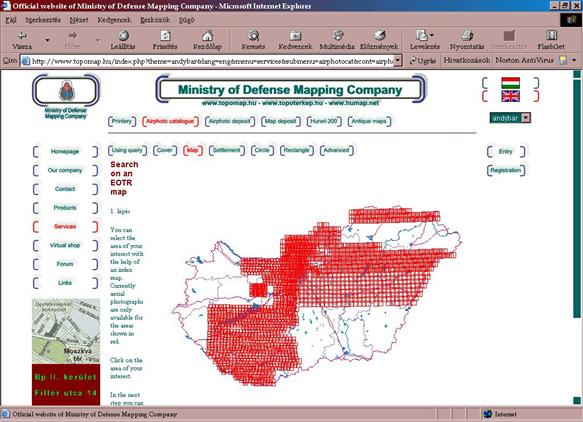
Internet catalogue of aerial photographs of the
Mapping Company of the Ministry of Defence
MS HDF
is responsible for technical supervision of survey camera aerial photography. Beside
authorisation and control of aerial photography of military purpose MS HDF is
also responsible for technical supervision in terms of security classification.
2. Map publishing enterprises
The competition in the map publishing business is as fierce as ever. Maps
of Hungarian territories using state base data have to be preceded by a
government licence issued by either of the two national mapping agencies as
stipulated by the 1996 Act on surveying and mapping. Computer technology is now
prevailing in both larger and smaller cartographic firms; in a viable mapping
company almost all phases of map production are now computerized. Below are
some examples of map publishing enterprises:




Contact address:
Ms. Gizella BASSA
GiziMap H-1279 Budapest 25, P.O. Boх 29.
Hungary
E-mail:
[email protected]
Customized maps (or atlases)
are generally derived from the original products of the publisher. Very often,
only the cover is different. Such specialized products are essential tools of
oil companies, auto clubs, car rental firms, real estate boards, distributing
or logistic companies.
 All products are in stock and can be
customized with your own cover in a very short time.
All products are in stock and can be
customized with your own cover in a very short time.

Contacts:
Szarvas András
CARTOGRAPHIC AGENCY
H-1149 Budapest, Répássy u.
2.
Tel./fax: (+36 1) 221 68 30, (+36 1)
363 06 72
E-mail: [email protected]
·
For the
best information on Hungarian map publishers it is advised to contact MATE, the
Hungarian Cartographic Association, an alliance of Hungarian cartographic
business people. Address: HU-2000 Szentendre, Dunakorzó 18., Hungary, President: Péter Vizi ([email protected] )
3.
Map collections, events on map history
3.1. The Map Collection of the National Széchényi Library
This collection, presently
numbering approximately 192,000 items, is based on the original donation of
Count Ferenc Széchényi, which contained a total of 1,500 items. The original
collection consisted primarily of 18th century maps depicting Hungary, the neighbouring countries
and castles. Additional donations, purchases and the legal deposit submission
of a copy of all newly printed books as well as maps resulted in the gradual
but steady increase of the collection.
The Map Collection was made
into an independent unit of the Library in 1939. It now contains 151,000
printed and 35,000 holograph maps, 5,000 atlases, 84 contour maps, 58 globes
and celestial spheres and 1,800 explanatory volumes.
The most important item among
the printed maps is the oldest map of our country, the woodcut "Tabula
Hungariae ad quatuor latera..." [sic] by Lazár, published in 1528. It
justifiably takes its place among the most outstanding cartographic creations
of its time and its wealth of place names makes it a source material of very
great value. Among the greatest treasures of the Collection are the 105 items
in the Enea Lanfranconi engraving collection, which also contains the creations
of numerous 16th-18th century map-makers including W. Lazius, János Zsámboky,
V.M. Coronelli, F. de Wit, Sámuel Mikoviny. They depict Hungary and its provinces.
The three editions (1664, 1684
and 1687) of M. Stier's Landkarten des Königreichs Ungarn. (Maps of the Kingdom of Hungary) come from the most eventful century of
our history. Of considerable cartographic importance, the large-scale map of
our country in 1709 by J. Ch. Müller is the first one to be based on actual
surveys and must be regarded as the first official map of Hungary. The incomparably beautiful
work of the Spaniard, C. Vasquez, Buda és Pest Szabad Királyi Várossainak
Tájleírása (Description of the Free Royal Cities of Buda and Pest), 1835, contains four sheets of maps,
each of which is an artistic masterpiece.
Among the unique, hand-drawn
maps, the earliest comes from the original collection of the donor. It is a
maritime map of 7 sheets, entitled Cartae Maritimae, a creation of G. Benincasa
of 1474. The two coloured Dutch portolan maps drawn on parchment by Gh. Hessel
in 1621 are among the earliest cartographic depictions of Australia. These maps are followed in
time by two Italian cartographic creations, E. Stenghri's Descriptio ac
delineatio totius Hungariae et Transylvaniae... of 1664 and G. Spalla's L'isola
Murakes of 1670. The latter is a work of unparalleled delicacy of drawing and
colouring. These are supplemented by the works of the most significant figure
in 18th century Hungarian cartography, Sámuel Mikoviny and by the works of
engineers, who in this and the following century did outstanding work in public
administration, land surveys and water regulation. These include Lőrinc
Bedekovich, Antal Balla, the brothers Kiss, József Beszédes and Mátyás Huszár.
Our atlas collection includes
the 1541 Lyon and the 1605 Frankfurt editions of the Geographia,
by the greatest of the ancient geographers Ptolemy; the 12-sheet Landtaflen
[sic], a woodcut atlas from the first half of the 16th century, published by
the Zurich press of Ch. Froschauer, and
one copy of the Lafreri atlas, considered to be a rarity.
Our collection also holds the
1595 edition of the A. Ortelius atlas, from the Platin press, a 1606 edition of
the G. Mercator atlas, hand-coloured, copper-engraved 17th century atlases from
the Blaeu press and creations by J. Janssonius, F. de Witt, M. Seutter and J.B.
Homann.
Among the valuable items of
the collection we find the Parvus atlas Hungariae..., the first Hungarian
pocket atlas, published in 1689 (the creation of Fabius Antonius Marchio de Colloredo
and Gábor Hevenesy) and two hand-drawn atlases: the first one, published in
1771, depicts the copper mines of the Oravica region, and the other one,
published in 1805 is the 120-sheet work of Antal Bauer depicting the
settlements of Bács-Bodrog County. The Magyar Átlása of Demeter Görög - Sámuel
Kerekes (1790-1811) and the Oskolai új átlás (New School Atlas) of Ézsaiás
Budai (1800) also deserve mention.
The two outstanding items of
our globe collection are the copper engraved globe with a diameter of 48 cm,
created in 1632 by M. Greuter; and the hand-drawn globe, created in 1862 by
László Perczel. This latter with a diameter of 132 cm is one of the largest
globes in Hungary.
Ms.
Katalin PLIHÁL Dr.
National
Széchényi Library
H-1827
Buda Castle, F Building
[email protected]
3.2. The
Cartographic Collection of the Maproom of the Hungarian Institute and Museum of War History
In its present form the Maproom
of War History was founded in 1954. The backbone of its total collection was
made up of two sets of earlier materials:
- a collection of fifty thousand items rightfully
belonging to Hungary was transferred from the War Archives /Kriegsarchiv/ of
Vienna to the Royal Hungarian Archives of War History /later: War Archives/
after the First World War;
- a set of sixty thousand objects of the Royal Hungarian
Cartographic Institute /later: Defence Mapping Institute/ was founded following
the First World War.
The collection of the Maproom
grew steadily partly by old maps /heritages, materials of other discontinued
collections/, partly by new acquisitions /military map series, aerial
photographs, other civil maps/. The total collection now numbers nearly
500.000. items /maps, atlases, globes, relief maps, professional journals,
books, aerial photographs/, and by sheer size it constitutes the largest
cartographic collection in Hungary.
Those military maps which were
forbidden to give to the researchers, because they had "secret"
qualifications, are free for research from 1992. Nowadays we have no classified
maps in our Maproom.
Subdivision of the Cartographic Collection
The majority of maps are grouped according to the
following geographical-regional divisions:
-
maps of the heavens, of the world - historical,
geographical atlases;
-
maps of the continents
-
maps of cities and their vicinities, travel
guide books
-
maps of
war history - maps showing battles, campaigns, military events - are further
grouped according to chronological order, following the classification of major
historical epochs.
Within the territorial divisions there are the following thematic
classes:
-
general political, administrative maps
-
physical maps
-
special thematic maps
One of the most important parts of the collection of
the Maproom is made up of the military series based on detailed field surveys,
showing both Hungarian and foreign territories. In Hungary
only the Maproom possesses complete series of the so-called first /1772-1784/,
the second /1806-1869/ and the third military surveys /1869-1884/.
The original coloured manuscript sheets of the first and
second military surveys are kept in the Kriegsarchiv in Vienna. Our Maproom has the colour copies
of the originals in the same size. Usefulness, aesthetic value of these copied
maps are ail but identical with those of the original ones.
The collection consisting of the military series
published by the Royal Hungarian Cartographic Institute, established after the
First World War, can also be considered as complete, both for basic survey and
derived scales.
The Maproom's collecting interests also cover military
series of different scales and publishing years published after the Second
World War in a different mapping and projection /Gauss- Krüger/ system.
In our collection as new items we have the NATO
compatible UTM coordinate system 1:50.000 and 1:250.000 scale military maps.
The 120.000-piece collection of aerial
photographs also has considerable value. A smaller part of them was made before
the Second World War, while most of them are copies of air photos made for
mapping purposes during the 1950s, '60s, ‘70s. and ‘80s.
Basic registration arrangement
of materials of the Maproom has been put into effect. Better orientation among
materials is assisted by a recording system, various study aid tools and index
maps which are continually updated.
Computer processing of the collection has also started.
Lists of geographical names of most sheets have also been processed,
alphabetically arranged and printed /close to 30.000 items/. We started the
elaboration of catalogue system in a My SQL database system.
A representative set of several maps of the Maproom has
been processed and written to CD (166 sheets). In addition the maps of the
first military survey of Hungary (for the present territory, 436 sheets, scale 1:28.800) are written
to CD as well.
The collection grows by some 4-5 thousand new items
yearly, a smaller part of them being old maps, new books and other
publications, while most of them are deposit copies of military series.
The Maproom, as a public
collection, is open to the public from 9 a.m. to 3 p.m. from Monday
to Thursday. The number of research people is about 1000-1100 in a year.
Black-and-white and colour photo and paper copies of maps are available on
order request.
The Maproom took part in the organization of different
exhibitions of the War History Museum, by lending maps.
Publications:
Annamária Jankó Ph. D: Study on
the second military survey. In: Hadtörténelmi Közlemények. 103-109 pp. 22001/1.
Exhibitions:
In March of 2000 –
exhibition on birthday of cartographer and engineer Mikoviny’s 300 anniversary
– in War History Museum
In September of 2000 -
Millenium Exhibition – Hungary on maps in a 1000 years period – evolution of military maps – Budapest, Technical and Economic University
- the same exhibition in Győr (2001), in Sopron (2002)
Annamária Jankó
Ph. D.
Director of the
Maproom
Hungarian Institute
and Museum of War History
H-IO14 Budapest,
Kapisztrán tér 2/4. Tel/Fax: +36 1 214 69 75
E-mail:
[email protected]
3.3.
Report on the Events Related to Map History in Hungary between 1999 and 2003
The past four years were very rich in
conferences and exhibitions, dealing with map history.
In
1999, on the occasion of the 300th anniversary of the peace treaty signed on 26 January 1699 in Karlóca, Hungary (today Srijemski
Karlovci, Serbia), a chamber exhibition was organised by the Map Room of the
National Széchényi Library. For the first time in Europe, the waring parties
(the Osman Empire, the Austrian Empire and Hungary) marked the national
borderline not only on site, but also represented it on the map attached to the
document.
In
2000, a joint exhibition and scientific session was organised by the National
Széchényi Library and the War History Institute and Museum on the occasion of
the 300th anniversary of the death and 250th anniversary
of the birth of Sámuel Mikovinyi. They published the proceedings of the
scientific session and the catalogue of the exhibition. The volume also comprises
the papers of a conference held in 1998 that analyzed the circumstances of
preparing the map: ”Mappa generalis regni Hungariae…” (General Map of the Hungarian Kingdom…) by János Lipszky.
In
2000, the Hungarian Society of Geodesy, Cartography and Remote Sensing organised
an exhibition: “One Thousand Years of Hungary in Maps”. Its catalogue
(52 pages) was published under the same title.
In
2001, the same material of “ One Thousand Years of Hungary in Maps”
moved around as a travelling exhibition in various Hungarian towns – Győr, Hódmezővásárhely, Eger. Finally, the collection was
exhibited in Paris as well.
(The title of the latter event and its catalogue was “La Hongrie depuis 1000
ans sur la carte géographique”).
In
2001, the Map Room of the National Széchényi Library organised chamber
exhibitions with the titles “National Maps – Maps of Provinces” and “Globes
kept in the Map Room”.
In
2002, the material of the exhibition “ One Thousand Years of Hungary in Maps”
was also sent to the town Sopron, as a part of a scientific session on the current status of the
scientific research in map history in Hungary. The convener of the conference was the Faculty of Forestry and
Sylviculture, West-Hungarian University.
In
2002, the Geological Institute of Hungary organised an exhibition in
Balatonfüred under the title: “Maps of Lake Balaton”. Title of the
catalogue: “Balatinus, Balaton Lacus, Peiso, Pelso – Balatoni térképek”.
Compiled and edited by Mrs. Jenőné Csongrádi, Balatonfüred, 2002. 32 p. ISBN
963 00 9727 4)
In
2002, on the occasion of the foundation of the National Széchényi Library, the
Map Room organised an exhibition from the maps donated to the nation by the
founder, Count Ferenc Széchényi.
In
addition to the above listed events, various scientific exhibitions and conferences
were held, where papers were delivered on map history. Among those events, the
most important was the one held in 1999, which was dedicated to the life and
activity of Johannes Honterus. It was Honterus, who published a map for the
first time in Hungary around
1539, under the title: “Chorographia Transylvaniae Sybenburgen”. The
Collection of Old and Rare Prints of the National Széchényi Library is the
keeper of the only copy in the world.
Publications on Map History:
1.
A magyar térképészek nagyjai. – Die Große der
Ungarischen Kartographie: Lipszky János – Mikoviny Sámuel. (Eminent
Hungarian Cartographers: János Lipszky and Sámuel Mikovinyi.) Edited by Katalin Plihál – Csaba Reisz
T. – Enikő Török. Budapest,
2001. 305 pp. ISBN 963 200 431 0.
- Térképkülönlegességek (Map Rarities) by Katalin Plihál. Budapest, 2002. 112 pp. ISBN 963 204 133 X
- Gróf Széchényi Ferenc térképeinek és atlaszainak katalógusa. 1.
kötet: Kéziratos térképek és atlaszok (Catalogue of Count
Ferenc Széchényi’s Maps and Atlases. Vol. 1. Manuscript Maps and
Atlases.) Edited by Katalin Plihál. Budapest, 2002. 442 pp. ISBN 963 200
450 7
- Gróf Széchényi Ferenc térképeinek és atlaszainak katalógusa. 1.
Köt. Kéziratos térképek és atlaszok (Catalogue of Count
Ferenc Széchényi’s Maps and Atlases. Vol. 1. Manuscript Maps and Atlases.
(CD-ROM version) Edited by Katalin Plihál. Budapest, 2002. 442 pp. ISBN 963 200
451 5
- Magyarország története térképeken (History of Hungary in Maps) by Árpád Papp-Váry. Budapest, 2002. 279
pp. ISBN 963 09 4387 5
- Magyarország általános térképének elkészítése a 19. század első
évtizedében. (Making the General Map of Hungary in the First
Decade of the 19th Century) by Csaba Reisz T. Budapest,
2002. 512 pp. ISBN 963 202 327 7
Information
about the events and publications concerning Hungarian map history is available
also on the Internet.
Allthough it is not a real map history event, but worth
mentioning here that the National Széchényi Library and the Lázár Deák
Cartographic Foundation have been jointly organising annual exhibitions from
the best printed and digital map products of the previous year every spring.
Katalin
Plihál
[email protected]
Budapest, 27th
February 2003.
4. Institutes of Higher Education in Cartography
4.1. Report of the Activities
of the Department of Cartography, Roland Eötvös University of Budapest (ELTE), between 1999-2003
4.1.1. Introduction
The
three basic duties of the Department are as follows:
- university-level
training of cartographers,
·
training
of cartographic knowledge to future teachers of geography and other students of
environmental sciences,
- supplying of
maps, digital images, webmaps and professional advice for educational and
scientific activities of the university's faculties.
The staff of the Department (full time, part-time and lecturers on contract)
numbers 13. Subjects of the cartography syllabus that require other
professional qualification than that held by the Department staff are taught
(entirely, by holding special courses, or by reading a few lectures) by noted
Hungarian and foreign scholars. 15 Hungarian and 6 foreign experts have contributed
to the training of cartography undergraduates between 1999-2003.
Training activities of the Department were expanded since the 1994-1995
schoolyear within the Postgraduate Degree School of Earth Sciences. In this
period 9 candidates got the PhD in cartography.
Within the past four years 5 students and 3 staff members took part in foreign
training projects at German and Portugal universities in the frame of ERASMUS co-operation.
István Klinghammer the head of
the department was elected the Rector of the University in 2000. He was
re-elected in 2003 for another 3-years period. He was elected for the member of
Leopoldina, the German Academy of Science in 2002.
The website of the department
(http://lazarus.elte.hu) was opened in 1995. This is the starting point of the
Hungarian cartography, the daily average data transfer is about 1.5 GBytes.
4.1.2. Training
The first independent
university department of cartography was established in 1953. The first
training syllabus was prepared in 1955, and it formed the basis of the training
of Hungarian cartography students until the early 1970s.
In 1973 cartography training
was changed as part of the general reform of university training. Cartography
training continued to be a 3-year course.
The Hungarian Act on Education
of 1986 has made it possible that cartography training become a 5-year course.
The first 10-semester course was launched in the 1988/89 schoolyear. We changed
our curriculum continuously since 1990 to fit it to the digital cartography and
we established a new curriculum in 2001.
Teaching of processes and
methods of computer-assisted cartography (automated surveying methods, computer
graphics, computer-controlled technologies, hypermedia) are secured by
technical acquisitions of the Department (GPS receivers and base station,
scanners, output devices).
4.1.3. Sub-program for
Cartography of the Doctoral School of ELTE
Cartography is
characterized by an essential variousness. Battles, geological formations, meteorological
phenomena and ocean currents are all chances for communication of cartographical
information.
If
you visit the homepage of the ELTE Department of Cartography, you can get a
sample of this variety, taking a view of whether the diploma works of our
students or the themes chosen by our Ph. D. students.
We
do not plan a radical change of our practice of training doctoral students, but
we are susceptible to any new tendency arising. Our purpose is to go before the
prevailing challenges and guide the way to those who work in practical
cartography. Indeed, most of our students, including the majority of Ph. D.
students, will find employment in the field of cartography (or in fields
related to it, e. g. informatics, environmental conservation, public administration);
some of them have even worked in these fields prior to being a student in our
department.
Most
of the staff of our department – researchers, professors, teacher-engineers –
participate actively in education, research and practical cartography. In
publication lists, beside traditional maps we can find electronic atlases and
multimedia cartographical publications financed by domestic or foreign
superiors (companies, founds, offices), whose preparation include theoretical
and practical work of the staff of our department.
Modern
education, especially doctoral schools and workshops surpassing even the higher
education, need strong developing of our technical resources, because this is
the only way to keep pace with the development of the general level of
techniques. This is why one of recent fundamental tasks of professors, Ph. D.
students and undergraduate students is to compete, compete and compete.
4.1.4.
Research
The
Department has undertaken research in the following three fields of subjects:
4.1.4.1. Aspects
of representation in thematic cartography (digital maps - electronic atlases)
Major results:
- Magyar Nagylexikon (Great Hungarian Lexicon), Vol. 8-15
(articles and maps), 1999-2002
- Térképeken a Világtörténelem (Hungarian edition of The Times
Atlas of World History), 1999
- Administrative Atlas of Hungary 1914, 2000
- World Atlas on CD-ROM (English/German/Hungarian), a cooperation
with Cartographia, 2001
- Multimedia historical CD-ROM of Finland and Hungary, 2002
- Cherising Hungary’s Heritage/National Parks and World Heritage Sites, 2002
4.1.4.2. Education in Cartography
Major results:
- International Workshop on MassMediaMaps, 1999
- Publishing a book about digital cartography (László Zentai),
2000
- Conference on "Teaching maps for children: theories,
experiences and perspectives beginning the 3rd millennium" in Budapest, 2002
4.1.4.3. Theoretical Cartography
Major results:
Being a landlocked country since 1920, Hungary has no significant marine
research. However, cartographical representation of marine areas has been a
repeated task of the Hungarian cartography.
In Hungary,
research supported by the Commission on Marine Cartography of the International
Cartographic Association started in 1989. As result of this, research on two topics
was completed in 2003. The two topics are:
1. “Multilingual gazetteer of geographical
names of marine areas and ocean floor…on CD-ROM”
2. IHO/IOC “Standardization of Undersea
Feature Names” English/Hungarian version; Bathymetric Publication No. 6.
Published by the IHB, Monaco
We intend to present our
results to the session of the ICA Commission on Marine Cartography, during the
21st International Conference in Durban, South Africa.
4.1.5. The Department’s other
activities in ICA
Commission members:
- Mátyás Márton:
Commission on Marine Cartography
- Jesús Reyes:
Commission on Cartography and Children
- Zsolt Török:
Commission on Theoretical Cartography
- László Zentai:
Commission on Education and Training, Commission on Maps and Internet
Conferences,
meetings:
- Organizing a
meeting of the ICA Commission on Education and Training in Budapest, 2000
- Conference on
"Teaching maps for children: theories, experiences and perspectives
beginning the 3rd millennium" in Budapest, 2002
- Organizing ICA
Executive Committee meeting, May 2003, Budapest.
István KLINGHAMMER
Professor and Head of Department,
László Zentai
Associate professor, Vice-head of Department
Mátyás MÁRTON
Associate professor
András Dutkó
Ph.D. student
Department of Cartography,
Budapest
4.2. Further institutions of higher learning in Hungary related to cartography:
4.2.1. The Department of
Geoinformatics, College of Surveying and Land Management at the University of
West Hungary (Székesfehérvár) is a college-level institute of higher
learning training surveyors for both the government and the profession in
general. The Department was established in 1994. As the first nation-wide
activity the NCGIA (The National Center for Geographic Information and
Analysis) CORE CURRICULUM adaptation was managed and published by the
Department. Its wide-level foreign contacts and training projects gained a
reputation for training in land information and GIS.
Contacts:
Postal address: Pirosalma
u. 1-3. Szekesfehervar
H-8000
Telephone: +36 22
348 271
FAX: +36 22
327 697
Electronic mail : [email protected]
4.2.2. Budapest University of Technology and Economics
The
legal predecessor of the University, Institutum Geometricum Hydrotechnicum
(Institute of Engineering) waws established by Emperor Joseph II (1780-1790) in
1782. Enginneers specialized in surveying and water regulation were trtained
for three years of study.
- Department of Geodesy and
Surveying: The basic educational task of the Department is to teach
the Surveying for civil engineering, surveying/GIS, and architecture
students, together with other obligatory and optional subjects.
Coordination of education for GIS military topographic engineers. The
Department offers courses in English, German and French languages for
foreign students.
Contacts:
H-1111 Budapest, Műegyetem rkp. 3. K.
mf. 16.
Tel: (36) 1 463 1146, Fax: (36) 1 463 3209
E-mail: [email protected]
- The Department of Photogrammetry and GIS is the
only university-level institution of learning in Hungary that specializes
in the training of engineers of surveying and GIS in the fields of
photogrammetry, remote sensing and GIS, but it also undertakes the
training of civil engineers and technical managers in GIS.
Contacts:
H-1111
Budapest, Műegyetem rkp. 3. K. mf. 16.
1521 Bp. Pf.: 91.
Tel: (36) 1 463-1187, Fax: (36) 1 463-3084
E-mail: [email protected]
5. Major Cartographic Events and News in Hungary 1999-2003
·
The Hungarian Cartographic Association (MATE),
an alliance of Hungarian cartographic business people, was set up in 1999. Its
primary aim is to ensure fair practice among actors of map publishing, and good
public-private partnership. It also annually organizes competitions for
professional prizes for cartographic products of the year.
·
On 1 January 2000 István Klinghammer, Professor and Chair of the Department of
Cartography at Eötvös Loránd University of Budapest, becomes the President of
the University
·
ICA Commission Education and Training met in Budapest in February 2000., Budapest
·
Within the international conference
"Teaching Maps for Children” the ICA Commissions Cartography and Children
and Gender in Cartography also met in Budapest’s Eötvös Loránd" University, in September, 2000
·
January 1, 2001:
Ministry of Defence Mapping Company is established (see 1.3.)
·
The 6th Global Spatial Data Infrastructure
(GSDI) Conference (GSDI6), entitled “From global to local”, was held in Budapest in September 2002 with 220
participants. The Conference marked a turning point in the development of GDSI
as a not for profit organization. The GSDI Association will give special
attention to develop capacity building efforts with particular reference to
obtaining resources for sustained capacity building in developing nations.
·
In conjunction with GSDI6 the ninth meeting of
the International Steering Committee for Global Mapping was also held in the
Hungarian capital city on 20 September 2002.
·
The luxurious volume „A History of Hungary on
Maps” by Árpád Papp-Váry is published in Budapest in December 2002.
·
Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest (ELTE), served host to the IMTA (International Map
Traders Association) EAME (Europe, Africa and the Middle East) Annual Conference and Trade
Show, 28 February-1 March 2003.
Budapest 2003
·
„Fine Hungarian Maps (Szép magyar térkép)”
competition. The Lázár Deák Cartographic Foundation, bearing the name of the
first Hungarian cartographer, and founded in 1994, annually organizes, together
with the National Széchényi Library, the competition for the most beautiful
maps of the year in several categories (tourism, science, atlases, digital
products). Awards are announced each year in mid-March.
·
Hungarian cartographers commemorated the 475th
anniversary of publishing the first Map of Hungary by Lazarus. A symposium at
the National Széchényi Library on 21 March 2003 highlited various aspects of
the map.
·
Hungary was proud to
host the ICA Executive Committee which held – on the premises of ELTE – a
meeting on 2-4 May 2003 and discussed preparations for the 12th General
Assembly of ICA and the 21st ICC. The meeting coincided with celebrations
marking the 50th anniversary of setting up the Department of Cartography at the
university.
·
In June 2003 the Hungarian government decided to
provide a loan for the production in 2003-2007 of digital (vectorized)
cadastral maps. covering the entire country
6. The Hungarian National Committee of ICA
President:
Dr.
Árpád Papp-Váry, director
Cartographia
HU-1590
Budapest, P.O. Box 80. Hungary
E-mail: [email protected]
Secretary:
Béla
Pokoly
Department
of Lands and Mapping
Ministry
of Agriculture and Rural Development
HU-1860
Budapest 55, P.O. Box 1. Hungary
E-mail: [email protected]
Hungarian members of ICA Commissions for 1999-2003
Education and Training
Mr. László ZENTAI Dr.
Department of Cartography, Eötvös Loránd University of
Sciences,
H-1117
Budapest, Pázmány P. sétány 2. VII. em. Hungary
E-mail: [email protected]
Map Production
Col. László BUGA
Ministry of Defence Mapping Company
HU-1276 Budapest 22, P.O. Box 85. Hungary
E-mail: [email protected]
Cartography and Children
Mr. Jesus Reyes NUNEZ,
Department of Cartography, Eötvös Loránd University of
Sciences,
H-1117
Budapest, Pázmány P. sétány 2. VII. em. Hungary
E-mail:
[email protected]
Gender and Cartography
Mrs. Gizella BASSA Gizimap
HU-1025 Budapest, Áfonya u. 1. Hungary
E-mail: [email protected]
History of Cartography
Ms. Katalin PLIHÁL Dr.
National Széchényi Library
H-1827 Buda
Castle, F Building
E-mail: [email protected]
Census Cartography
Mr. Tamás TÓTH
Central Statistical Office, Dept. of Census
Budapest, P.O.
Box 51., H-1525 Hungary
E-mail: [email protected]
Marine Cartography
Mr. Mátyás MÁRTON Dr.
Department of Cartography, Eötvös Loránd University of
Sciences,
H-1117
Budapest, Pázmány P. sétány 2. VII. em. Hungary
E-mail: [email protected]
Spatial Data Standards
Lt.-Col. István KÁDÁR
Mapping Service of the Hungarian Defence
Forces
H-1525 Budapest 114, P.O. Box 37.
E-mail: [email protected]
Theoretical Cartography
Mr. Zsolt TÖRÖK Dr.
Department of Cartography, Eötvös Loránd University of
Sciences,
H-1117
Budapest, Pázmány P. sétány 2. VII. em. Hungary
E-mail: [email protected]
Maps and the Internet
Mr. László ZENTAI Dr.
Department of Cartography, Eötvös Loránd University of
Sciences,
H-1117
Budapest, Pázmány P. sétány 2. VII. em. Hungary
E-mail: [email protected]
Map Generalization
Mr. Zoltán BAKÓ Dr.
Ministry of Defence Mapping Company
H-1525 Budapest 114, P.O. Box 37.
E-mail: [email protected]
Mapping from Satellite Imagery
Ms. Éva CSATÓ Dr.
Institute of Geodesy, Cartography and Remote Sensing,
HU-1149 Budapest, Bosnyák tér 5. Hungary
E-mail: [email protected]
National and Regional Atlases
Mr. László BASSA
Geographical Research Institute of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences
H-1112 Budapest, Budaörsi út 43-45. Hungary
E-mail: [email protected]

 1:10 000
Analogue and Digital Topographical Map Status Description
1:10 000
Analogue and Digital Topographical Map Status Description